What is a Geomembrane?

Geomembranes are often included as part of the engineered barrier system for modern landfills (Rowe, 2001). As defined in ASTM D4439-00, a geomembrane is “an essentially impermeable membrane used with foundation, soil, rock earth or any other geotechnical engineering-related material as an integral part of a man-made project, structure or system”.
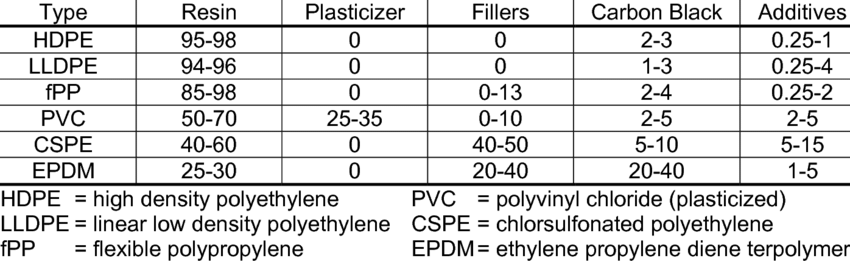
There are various types of geomembranes including high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorinated polyethylene (CPE), chlorosulphonated polyethylene (CSPE), ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM), polypropylene (PP), linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), medium-density polyethylene (MDPE) and, more recently, the bituminous geomembrane.
Why does geomembrane degrade?
Degradation of HDPE geomembrane is typically caused by oxidation, which is primarily driven by either thermo-oxidative ageing (temperature-based) or photooxidative(UV exposure-based). Degradation may increase the likelihood of stress-cracking or failure and limiting exposure of the geomembrane to sunlight and heat is the most effective way to maximize its lifespan.
The service life of the geomembrane is defined as the half-life.
The lifespan of a geomembrane liner is defined by three stages:
- Stage 1: Depletion time of antioxidants
- Stage 2: Induction time to onset of degradation
- Stage 3: Time to reach the service life, specified as the 50% degradation point (half-life) of the geomembrane
Factories for the degradation of geomembrane
Geomembrane degradation is caused by oxidation, which is promoted by exposure to heat and UV radiation.
Conclusion
HDPE geomembranes are extremely durable products, designed with service lives up to several hundreds of years under ideal conditions. The service life of an HDPE geomembrane is typically defined as its half-life, which is the point at which 50% of the geomembrane has degraded.
The primary cause of degradation of lining systems is oxidation of the geomembrane, which eventually weakens the membrane and allows stress cracks to form. Oxidation is inhibited by limiting exposure of the geomembrane to UV radiation and open-air environments and maintaining lower average ambient temperatures around the lining system. HDPE is chemically resistant to most substances, especially at lower temperatures (20°C or less), and chemical degradation of lining systems is generally considered a non-issue for most municipal uses.